If there’s the slightest sign of defect or decrease in performance in your car, it should be addressed immediately. If not, it could turn into a real “illness.”
Which is why it’s a good thing to carry a diagnostic tool like an OBD-I for your vehicle. But what exactly is an OBD-I? What does it do? Can you use it on all types of vehicles? How is it used? Philkotse.com will discuss the answers to that right here:
There are different types of diagnostic scanners in the market. Some can have different purposes than others while some may have everything you will ever need.
One of the common examples is OBD-I. The abbreviation OBD stands for Onboard Diagnostics I. OBD-I, including other code readers and scanners are devices that are capable of pulling info from your car.
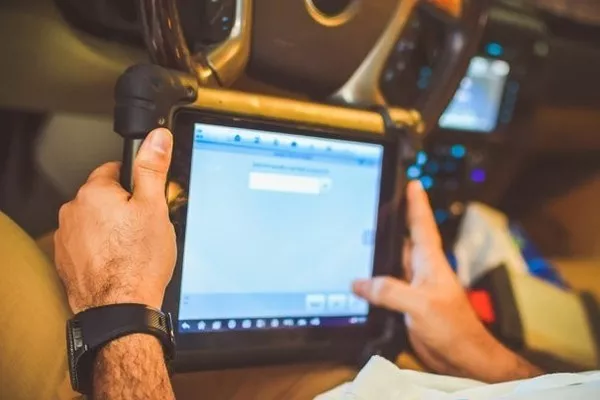

There are different types of diagnostic scanners in the market
This important info is stashed in your vehicle’s onboard computer. If there’s anything wrong with your vehicle, your onboard computer would know about it.
So for you to know that info, you’re going to need either a scanning tool, a code reader or any diagnostic tool that works. These devices will be used to pull out the trouble codes so you can understand what’s really wrong with your vehicle.
How to onboard diagnostics and OBD-I scanners came to be
A lot of the vehicles that were manufactured before 1996 had a first-generation onboard diagnostic system. These are generally called OBD-I. The very first OBD-I system was estimated to show up sometime in the later 1970s and earlier parts of the 1980s.
Every manufacturer at the time was responsible for developing its own interface technology. That means, even though these bunch of systems shares a general name of OBD-I, they are actually not so similar.
Since there was barely any standard for this system at the time, each manufacturer had their own insights on OBD-I jacks and plugs. Not only that, the OBD-I scanners at the time we're supposed to work with vehicles that were a particular model and make.
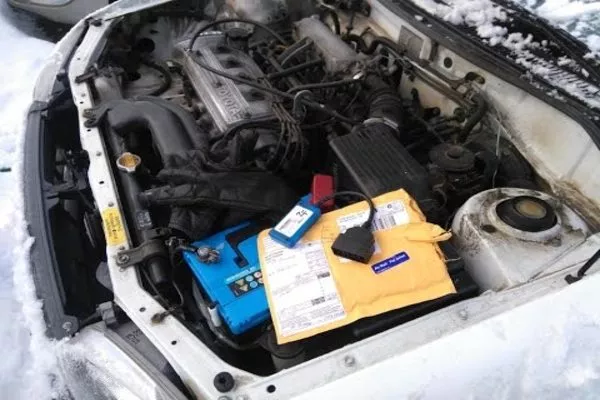

An OBD-I scanner purposely fitted to work with a Toyota of particular make
For example, let’s say you have an OBD-I scanner purposely fitted to work with a Toyota of particular make and model. Your OBD-I scanner will definitely not work when used in other vehicles like a Suzuki or a Ford.
But there is also good news. In a lot of cases, one won’t actually require an OBD-I scanner if you only need the codes. The downside is that every OEM had its own way of pulling codes without the use of diagnostic tools. So this can still be complicated.
>>> Related: How to choose OBD-2 Scanner in the Philippines & 10 recommended products
How do I select the perfect OBD-I scanner?
Just like we said earlier, OBD-I scanners don’t work like OBD-II devices that are compatible with most vehicles. But some of these OBD-I scanners are actually designed to be a bit more useful than the original tools.
It may not work as well as OBD-II scanners. But it can work with a few models and makes rather than just one.
OBD-I scanners that are specific to their OEM make use of software and hardwired connectors. These are only capable of syncing with a couple of onboard computers coming from a single manufacturer.
If you are not a total expert when it comes to automobiles, it’s best to settle for an OEM-specific OBD-I scanner. Make sure you pick out the best one that will work in your car. These can easily be purchased from auto supply stores and even in online marketplaces.
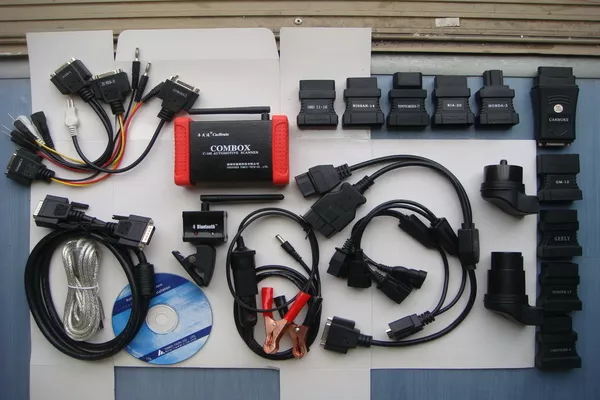

Multi-OEM and universal scanners offer interchangeable software and connectors
>>> Related:
- 8 essential tips when buying car accessories online
- Top 3 Tips on Getting the Best Deals on Car Accessories in Banawe Street
Multi-OEM and universal scanners offer interchangeable software and connectors. Simply put, this can take care of more than just one make or vehicle model.
There are also scanners that offer interchangeable modules or cartridges. These are used to switch between the different OEMs. OBD-I scanners that can work with more than one OEM is more expensive than its simpler counterpart.
In fact, the price can even go to a couple of thousands of pesos for a scanner that works with OBD-II and OBD-I systems.
This, however, is a recommended option only for those who really need it. An example of this is automotive mechanics who make a living out of fixing vehicles.
What does an OBD-I scanner do?
OBD-I scanners definitely lack a lot of features. If compared to OBD-II scanners, the latter would be more suggestible, but this is all because of the limitations associated with OBD-I systems. Most OBD scanners will be able to get a hold of freeze frame data and other information.

If there’s the slightest sign of defect or decrease in the car performance, it should be addressed immediately
>>> Related: Why you should get an OBD-2 scanner for ECU-equipped cars?
The simplest OBD-I scanners in the market work like simple code readers. All this can do for the user is to display the trouble codes. As a matter of fact, OBD-I scanners don’t even show the numbers on a screen.
It’s supposed to have some type of light emitter that blinks. After grabbing the codes, it will give you the trouble codes through blinking. You need to count this so you have a reference.
There are also OBD-I scanners that are capable of clearing codes, while there are also others that will require you to work. This is usually doable by performing a very basic procedure. You will be obliged to disconnect the battery or remove the ECM fuse.
OBD-I scanners definitely lack a lot of features. If compared to OBD-II scanners
>>> Related: 10 recommended software for OBD II scanner
Combination OBD-II and OBD-I Tools
These days, there are already scan tools and code readers that are capable of handling both OBD-II and OBD-I systems.
These types of scanners come with software that can handle even pre-onboard computers from numerous OEMs. This can also handle software with the ability to interface with post-1996 OBD-II systems as well as multiple connectors.
Most professional automotive and technicians use a combination tool. This is because it’s a more versatile choice rather than having multiple tools. These, however, can be expensive depending on their functionalities.
Recent posts
- A summarized guide to all of your car parts & functions Aug 18, 2023
- 5 must-know tips if you want to avoid buying fake car parts Aug 09, 2022
- 9 common car sensors and the facts that you might not know Aug 17, 2022
- 10 Must-know Car Engine Sensors Aug 09, 2022
- Top 6 must-have car accessories Dec 22, 2020












