Car improvement and the quest to make driving safe by all means is an ongoing process and today, thanks to the technology available, we might already be in close range in meeting the goal. A big credit goes to the ESC or Electronic Stability Control systems that have been incorporated to most of the cars today.
1. What is ESC?
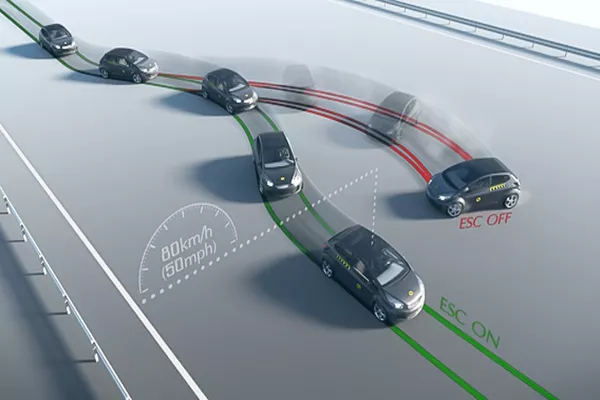
This system helps the drivers to avoid car crashes by decreasing the risk of skidding. This also reduces the loss of car control during over-steering.
Technically, the ESC gets activated when the driver loses control of the car and thanks to the computer-controlled mechanism; individual brakes are then applied to gear the car safely on track less the risk of fish-tailing.
ESC is considered as an active safety enhancement that should reduce the count and lower the severity of vehicular accidents. It provides traction and anti-skid sustenance for the extreme cases of oversteering and understeering. The button for ESC is a car with wavy lines sign.
Oversteering is when the car continually turns beyond the driver’s steering input due to its rear end sliding away. Understeering meanwhile is when the car turns less than the driver’s steering input due to inadequate traction.
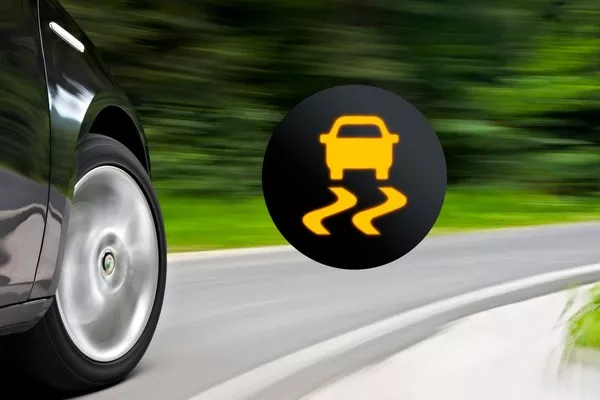

ESC is considered as an active safety enhancement
2. When will ESC be useful?
The Electronic Stability Control of the car again provides additional support and control to the driver. It should make them more confident for situations that are otherwise very challenging and sometimes impossible. ESC should come in very helpful in the following driving scenarios:
The driver underestimated a curve and approached it too fast thus needing to steer more aggressively than usual.
- A surprise on the road causing the driver to swerve quickly to avoid or miss things like an animal, a car pulling out of the driveway or another motorist that cuts in front of the car.
- One of the car wheels hits a patch of ice sending the car into a spin.
- Poor road conditions like gravel patches, holes, and factors due to repair and natural elements
- Miscalculations of the driver.
The ECU of the car again provides additional support and control to the driver
>>> Read more: 12 safety features of modern cars you should understand.
3. How does ESC work?
With the use of intelligent sensors, the ESC would automatically detect any problems with the car’s control, and it will instantly apply the brake to the applicable wheel allowing the driver to regain control on the projected path.
The ESC systems are composed of a good number of subcomponents supervised and controlled by the Electronic Control Unit or ECU.
These subcomponents are:
Yaw Sensor – this measures the car’s movement specific to its side to side motion.
Wheel Speed Sensors – this measures that speed of each wheel’s rotation.
Steering Angle Sensor – this monitors the steering input
Hydraulic Unit – this increases the braking or decreases the wheel speed.
The ECU is responsible for retrieving and consolidating the data from these sensors and continuously determines if there is a variance between the driver’s steering input and the actual direction of travel.
It will be up to the wheel speed sensor to report back to ECU if there are wheels that are spinning more quickly than usual or than the other wheels. This is a sign of the wheels dropping in its traction.
If the ECU concludes that something is off, it will send a signal to the hydraulic unit to exert more brake force to the wheel in question. Other updated systems might even initiate a drop in engine power.
Electronic Stability Control Technology(ESP, DSC, ESC, A-TRC)
In cases where the ECU senses an oversteering, it will send a signal order to put on the front outside break to counter the traction loss on the rear wheels. In an understeering case, it will be the inside rear brake that will be pressured so the car would turn as directed by the driver’s steering input.
Note though that not all ESC systems are the same. Yes, the hardware might be similar, but there are variations on how it works and responds. The level of its efficiency depends on a lot of factors too like the traction between the car and the road, the condition of the tires and the road environmental circumstances.
>>> Related: Car with wavy lines symbol: Meaning, function, and importance
4. Is ESC effective?
Based on the studies and the numbers, ESC is indeed a great asset to cars. It is instrumental in reducing the number of vehicular and road-related crash accidents. ESC cut life-threatening single-vehicle crashes by 49%, and fatal multiple vehicle car crashes by 20%.
ESC not only lowered the statistics of crashes but has significantly prevented rollovers reducing the numbers by almost 72%.
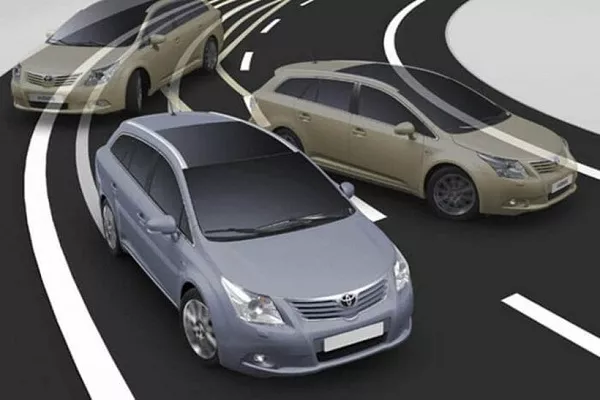

ESC is indeed a great asset to cars
>>> Also check: Signs of failing cruise control and how to use it properly.
5. Is ESC full-proof?
No, it’s not. Like any other system, ESC has its limitations, and the driver is one of the most significant and uncontrollable restrictions of this system. There is no question of its effectivity but, is the driver working appropriately with this system?

The ESC cannot control the driver’s attitude when it comes to driving
The ESC cannot control the driver’s attitude when it comes to driving. Specific behaviors like speeding, distracted driving, tailgating, and fatigued driving are not something that the ESC can regulate. During the process of stabilizing the vehicle, ESC can only work with whatever traction is available.
It does not create traction. ESC will have no rule nor will it compensate any mishaps brought about by irresponsible driving. Drivers should still be attentive and should not solely rely on their car’s ESC to navigate through the roads.
6. Different Names for ESC
The Electronic Stability Control system may be referred to differently depending on the brand of the car and sometimes even on the country. Here are just some of the names it goes with:
|
Names for ESC
|
Car brands
|
|---|---|
|
Dynamic Stability Control or DSC
|
Ford, BMW, Mazda, and Jaguar
|
|
Electronic Stability Program or ESP
|
Hyundai, Kia, Jeep, Saab, and Mercedes Benz
|
|
Vehicle Dynamic Control or VDC
|
Nissan and Subaru
|
|
Vehicle Stability Control or VSC
|
Suzuki and Toyota
|
|
Active Stability Control or ASC
|
Mitsubishi
|
|
Electronic Stability Programme or ESP
|
Dodge
|

For Ford models, ESC is called Dynamic Stability Control
Everyone traveling and driving or has a car should appreciate all the efforts that are being dedicated to positive technologies like the ESC to improve the quality of safe driving. Bear in mind though that these are just added enhancements to make the overall driving experience safe and secure.
One should always practice responsible driving because being out in the road regardless as a driver or as a passenger is still a risk. This article from Philkotse.com aims to explain the importance, effectiveness and how the ESC works.
Recent posts
- 7 must-have active safety features in modern car Apr 13, 2021
- All you need to know about ABS - Anti-lock braking system Feb 27, 2019
- Learn about the Hill-start Assist Control (HAC) & Downhill Assist Control (DAC) Feb 20, 2019
- Real car deal: 7 Pros & Cons of car Engine control unit (ECU) Jan 19, 2019
- Top most essential car safety features to have in your car Jul 09, 2018












