Brakes in cars and other types of engines are essential for its smooth operation. Knowing what kind of brake your vehicle has, will enable you to determine the right way of handling it or fixing it once it breaks.

Brakes in cars and other types of engines are essential for its smooth operation
Moreover, it lessens the occurrence of accidents caused by broken brakes. This article from Philkotse.com will give you helpful information about hydraulic and electromagnetic brakes for your reference.
To quickly grasp the concept, we will first discuss hydraulic brakes separately.
What is the hydraulic brake?
The hydraulic brake is a braking system used in cars that requires a special kind of liquid to slow down or to bring the vehicle into a halt.
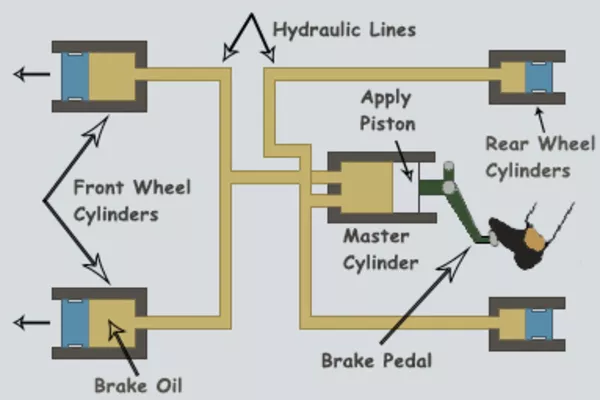
The hydraulic brake is a braking system that requires a special kind of liquid to slow down
>>> Find more: 4 rules that every Filipino driver should know about braking
What are the parts of a hydraulic braking system?
These are the typical components included in a conventional hydraulic braking system:
| Components | Function |
|---|---|
| Brake pedal | Where the driver extends his foot to exert mechanical force into the pushrod |
| Push Rod | This continues the transferring of the mechanical force to the servo and then to the master cylinder |
| Servo | Called the vacuum booster helps the driver in supplying extra power to the system |
| Master Cylinder | The pistons, seals, and springs inside the master cylinder enables the non-hydraulic force applied by the foot extended by the driver on the brake pedal to be transformed into hydraulic force and eventually aids in creating pressure for the force to be transported to the hydraulic lines |
| Reservoir | It holds sufficient fluids to prevent air from entering the brake system |
| Hydraulic Lines | Serves as the carrier of the hydraulic liquids to the front and rear brakes |
| Wheel brakes | Mounted in the interior part of the wheel that contains a wheel drum. The wheel drum does not rotate, and when it collides with the shoes, it brings the car into a halt by friction |
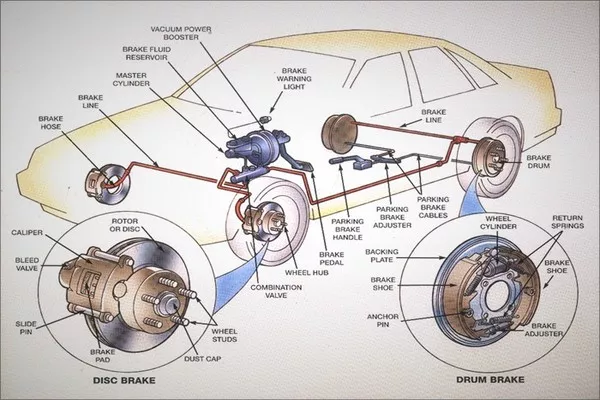
The different parts of the hydraulic braking system
>>> More to read: How to use your car brakes properly
How does the hydraulic braking system work?
By pressing the brake pedal, the mechanical force exerted here is then transferred to the pushrod and into the servo. The servo applies additional power to the master cylinder to supply a sufficient amount of pressure to carry the hydraulic liquids to hydraulic lines.
The hydraulic fluids that travel from the hydraulic lines will then reach the brakes of the car that creates friction through the wheel brakes, thus, causing the vehicle to stop.
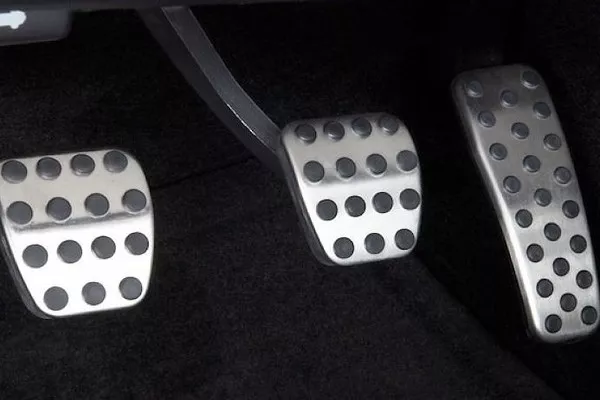

By pressing the brake pedal, the mechanical force exerted here is then transferred to the pushrod and into the servo
When the foot on the brake pedal is released, an opposite action is conducted. The hydraulic fluids in the hydraulic line will be reduced, and it will go back to its original position because less force is exerted to the master cylinder. By releasing the brake pedal, it will result in the car to continue its motion.
>>> Recommended for you:
- 6 warning signs of a poor braking system
- 6 signs showing that your car's brake system needs maintenance
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the hydraulic braking system?
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
What are electromagnetic brakes?
Electromagnetic brakes are the mechanical portion to stop or at least slow the rotary motion. It requires electric power to work. Hence, it is known as a power-on brake.
It is usually used in packaging and food-processing machinery, medical equipment, servo motors and robotics, elevators, and escalators. However, today it is also employed in cars.

Electromagnetic brakes are the mechanical portion to stop or at least slow the rotary motion
What are the components of the electromagnetic braking system?
| Components | Function |
|---|---|
| Stator | where the coil is built that becomes magnetic and eventually produces a magnetic force |
| Lining | the part that covers the inner surface of a particular material |
| Armature | where the stator is pulled due to the electromagnetic force |
| Plate Spring | placed between the armature and armature hub |
| Armature hub | it is attached to the axis and rotates together with the axis when the power is off |
>>> Check out:
- Disc Brakes vs Drum Brakes: How are they different?
- Things you might not know about brake pads and car rotors
How does electromagnetic brake work?
When the power is off, the axis attached to the armature hub together with the armature is rotating freely. The stator generates a magnetic force once the electric power is on.
Due to the magnetic force produced, the armature that rotates with the axis is being pulled to the stator. The rotary motion is brought to a halt because of the brake torque created by the friction between the stator and armature.
Due to the magnetic force produced, the armature that rotates with the axis is being pulled to the stator
Advantages and disadvantages of Electromagnetic Braking System
Electromagnetic brakes have their fair share of advantages and disadvantages. Those are:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Recent posts
- Electronic Brake Force Distribution and what you need to know Jun 09, 2021
- How to fix common problems with car's clutch hydraulic Jan 15, 2021
- Organic vs Ceramic brake pads - Which one is the best for your car? Jan 29, 2021
- Safety tips: How to drive when your car brakes are malfunctioned Nov 30, 2022
- 7 steps to deal with the car brake noise Nov 30, 2022












